 |
| This role supports the tools used by the project. This includes selecting and acquiring tools, configuring and setting them up, and verifying that they work. |
| Role Sets: Production & Support |
|
Relationships
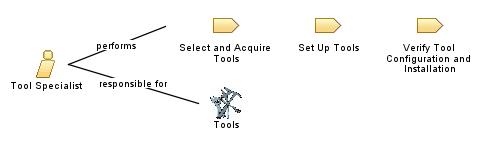
|
| Modifies |
|
Main Description
Staffing
| Skills |
An individual playing the role of a Tool
Specialist needs to have a broad set of skills. This includes an understanding of the underlying processes used by
the project, and for this training might be required prior to project startup. General systematic analysis skills are
beneficial when comparing and selecting tools for the project. Knowledge of the development platform(s) is required, on
networking issues in particular. A person acting as a Tool Specialist also needs good communication skills and a
'service-minded' attitude, since she or he is likely to be a support contact point for the project members, on
installation and other tool troubleshooting issues.
|
| Assignment Approaches |
The Tool Specialist role can be assigned
in the following ways:
-
Assign one or more staff members to perform both the Tool Specialist and Implementer roles. This is a commonly adopted
approach, especially in small-to-mid-sized teams, and capitalizes on the common development skills that Implementer
role shares with this role.
-
Assign one staff member to perform the Tool Specialist role only. This is a commonly adopted approach
and is particularly suitable for large teams or smaller teams where effective tool support and process automation
is a key aspect of the projects development plan.
|
More Information
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1987, 2006. All Rights Reserved.
|
|

